Sciatica: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Pain Relief
What is Sciatica?
 Sciatica is a type of nerve pain caused by irritation or damage to the sciatic nerve. It may also cause tingling or numbness in your butt or back, which may extend down your leg in addition to pain. It’s also possible for symptoms to get more serious.
Sciatica is a type of nerve pain caused by irritation or damage to the sciatic nerve. It may also cause tingling or numbness in your butt or back, which may extend down your leg in addition to pain. It’s also possible for symptoms to get more serious.
The longest and thickest nerve in your body is the sciatic nerve. It has a width of up to 2 centimeters, which is comparable to the width of an American penny or a British pence coin. It is not a single nerve, despite its name.
Causes of Sciatica
Herniated Discs
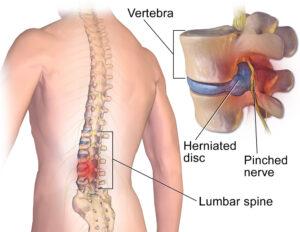
Sciatica is often triggered by herniated spinal discs. These discs, acting as cushions between vertebrae, may bulge or rupture, putting pressure on the sciatic nerve and causing discomfort.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis, a condition where the spinal canal narrows, can also contribute to sciatica. This narrowing squeezes the nerves, including the sciatic nerve, resulting in pain and other symptoms.
Piriformis Syndrome
The piriformis muscle in the buttocks can irritate the sciatic nerve if it spasms or tightens, leading to piriformis syndrome and sciatic nerve compression.
Spondylolisthesis
In spondylolisthesis, one vertebra slips forward over another, potentially compressing the sciatic nerve and causing sciatica symptoms.
Symptoms of Sciatica
Recognizing sciatica is vital for effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp pain – Radiating from the lower back down to the leg.
- Numbness and tingling – Often felt in the leg or foot.
- Muscle weakness – Impacting mobility and strength in the leg.
Treatment Options
Conservative Approaches
Sciatica often responds well to conservative measures, including:
- Physical therapy – Targeted exercises to strengthen muscles and relieve sciatic nerve pressure.
- Anti-inflammatory medications – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Heat and cold therapy – Alternating hot and cold packs for relief by reducing inflammation and enhancing blood flow.
Medical Interventions
In severe cases, medical interventions may be necessary:
- Epidural steroid injections – Targeting affected areas to reduce inflammation.
- Surgery – Considered in persistent pain and structural issues.
Pain Relief Strategies
Exercise and Stretching
Engage in regular stretching exercises and incorporate low-impact aerobic exercises for significant pain relief. These activities enhance flexibility, strengthen muscles, and improve overall spine health.
Mind-Body Techniques
Explore mind-body techniques like yoga and meditation for relief by reducing stress and promoting relaxation, crucial in minimizing sciatica symptoms.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Make ergonomic adjustments in your daily life, emphasizing proper posture and supportive furniture to prevent sciatica symptom exacerbation.
What are the risk factors for sciatica?
- Age – As people age, the spine undergoes natural wear and tear, leading to conditions like herniated discs and bone spurs, which can compress the sciatic nerve.
- Occupation – Jobs that require heavy lifting, prolonged sitting, or twisting of the back may increase the risk of developing sciatica.
- Obesity – Excess body weight can put pressure on the spine and contribute to the development of sciatica.
- Diabetes – This condition can lead to nerve damage, increasing the likelihood of sciatic nerve compression.
- Sedentary Lifestyle – Lack of regular exercise and physical activity can contribute to weight gain and muscle stiffness, increasing the risk of sciatica.
- Improper Posture – Poor posture, both while sitting and standing, can strain the spine and contribute to the development of sciatica.
- Pregnancy – The extra weight and pressure on the spine during pregnancy can lead to compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Injuries – Trauma or injuries to the spine, such as fractures or dislocations, can lead to sciatica.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can sciatica be completely cured?
- While a complete cure depends on the underlying cause, effective management through conservative measures and medical interventions can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Is surgery the only option for severe sciatica?
- Surgery is considered in severe cases, but it’s not the sole option. Other interventions are explored first.
How long does it take for sciatica to improve?
- The duration varies, but many experience improvement within weeks with proper treatment and self-care.
Can sciatica be prevented?
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining good posture, and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of developing sciatica.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of sciatica is essential for effective care and relief. Taking an integrated approach to sciatica is essential to improving your quality of life, whether that approach is conservative, involves medical interventions, or involves holistic pain relief strategies. At Painmedic Pain Clinic, we are committed to providing clear and detailed treatment plans to help you navigate and ease sciatica symptoms effectively.


